Browse Interferometric (InSAR) Data Quality Metrics
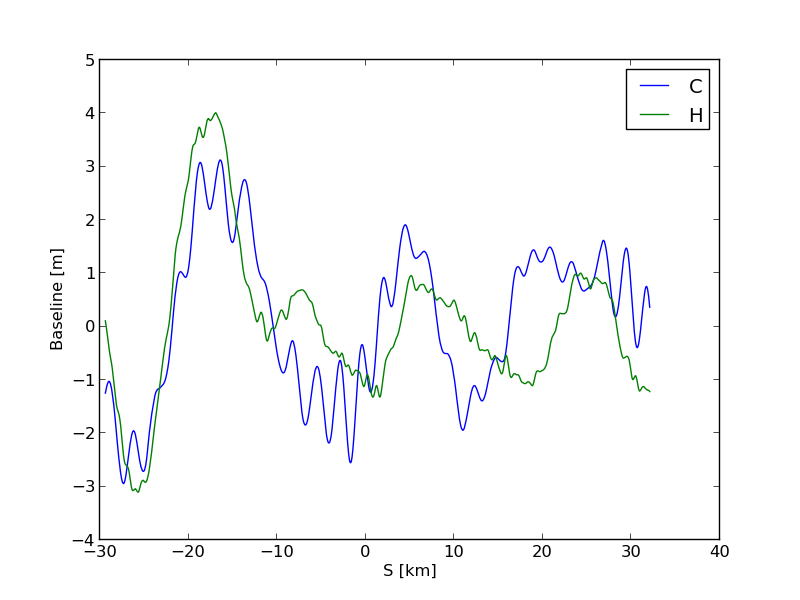
Baseline
The interferometric baseline in the cross-track (C) and
vertical (H) directions as a function of the along-track coordinate (S).
Example:
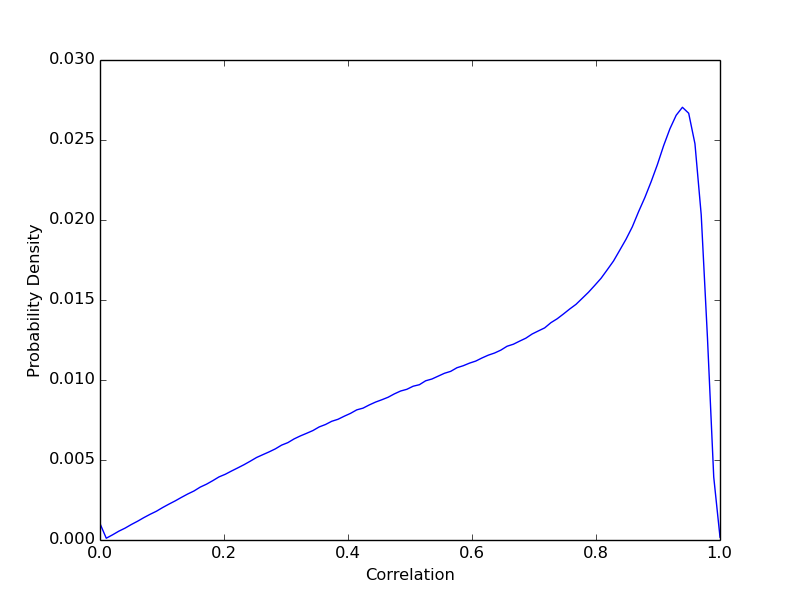
Correlation (Interferometric Coherence)
The probability density function (PDF) of the interferometric correlation.
The correlation is estimated over a sliding window and is not corrected for
phase gradients or other effects. The PDF is estimated with a histogram.
Example:
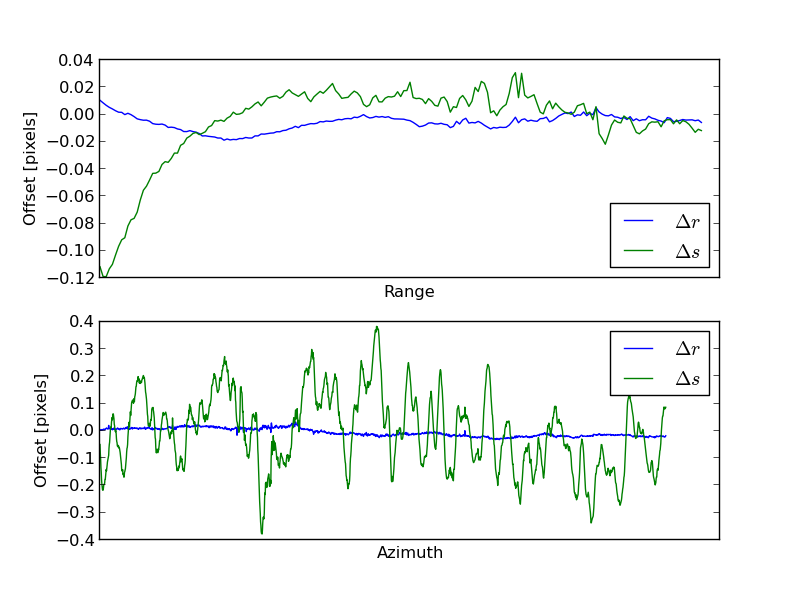
Offsets
Profiles of the relative image registration offsets. The two-dimensional
offset field is estimated with an amplitude correlation based matching
algorithm. Outliers are detected and removed, and average profiles in the
range and azimuth directions are shown in the figure.
Example:
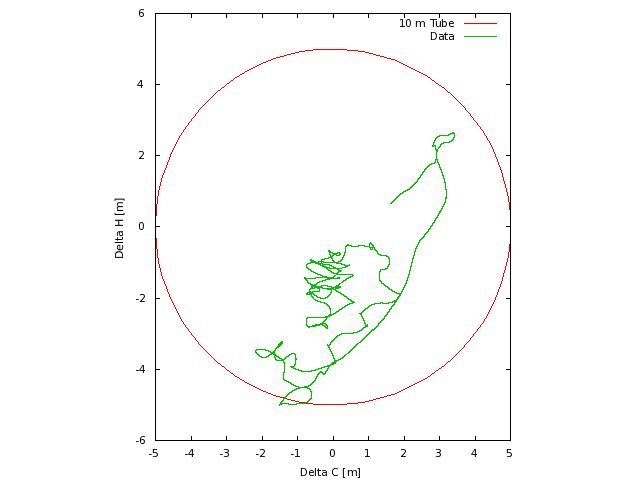
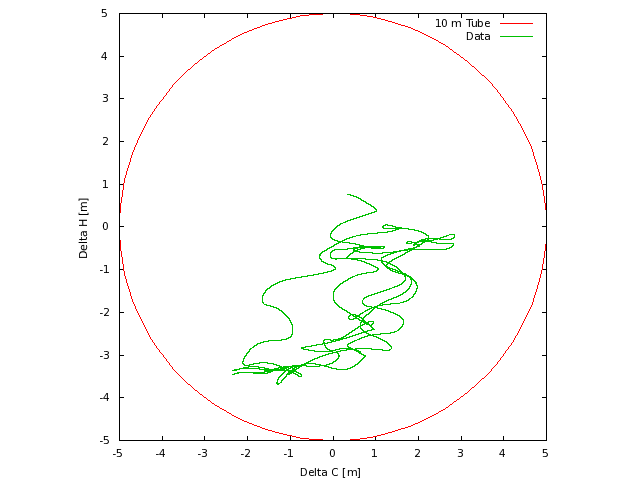
Position
The position of the radar relative to the planned track, with the required
ten meter tube shown for reference.
Example:
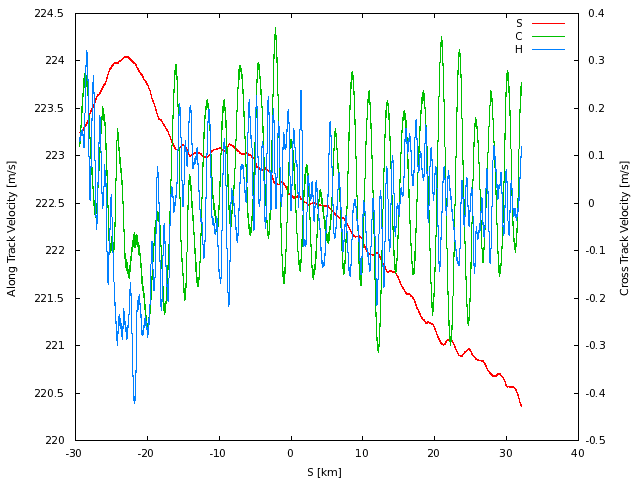
Velocity
The velocity of the radar. The left axis measures the along-track
velocity (S), while the right axis measures cross-track (C) and vertical (H)
velocities ten meter tube shown for reference.
Example:
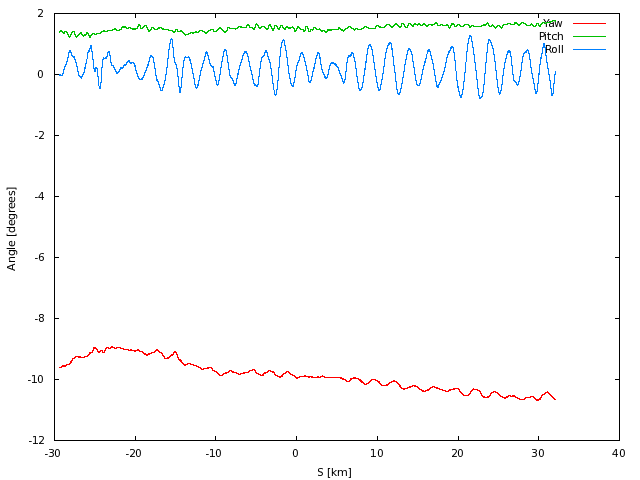
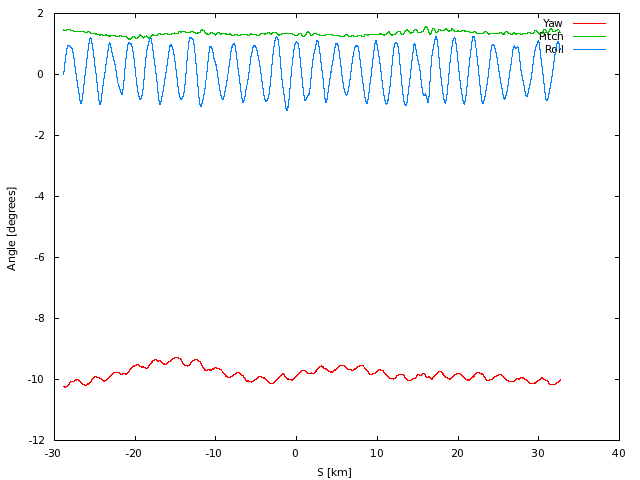
Attitude
The orientation of the radar. Yaw and pitch determine the electronic
steering angle and processing Doppler curve.
Example: